Migraine: Understanding the Pain, the Triggers, and How to Take Back Control
If you’ve ever had a migraine, you know it’s not just a headache. It’s that kind of pounding, throbbing pain that makes you want to crawl under a blanket, close your eyes, and pray the world would quiet down for a minute. And if you haven’t had one yet—well, consider yourself lucky, because those who do experience migraines know just how life-stopping they can be.
But here’s the interesting part: once you understand what actually triggers and how to manage them, the whole condition becomes a lot less frightening—and a lot more manageable.
Let’s break it down in a simple, friendly way.
What Exactly Is a Migraine?
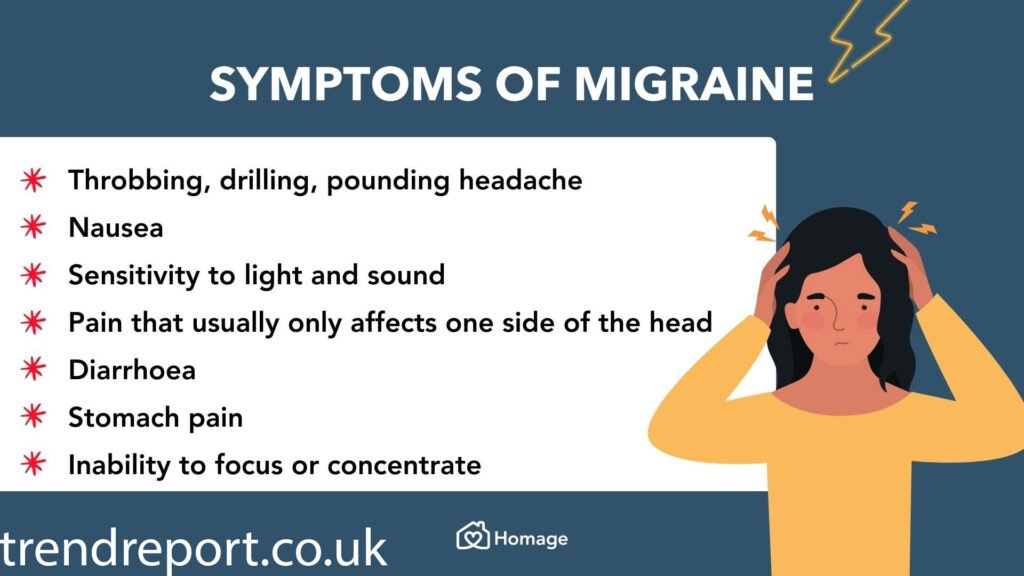
A migraine is a neurological condition that causes intense, often debilitating headaches. The pain usually comes with other symptoms like:
-
Sensitivity to light and sound
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Blurred vision
-
Dizziness
-
Aura (flashes of light, zigzag lines, or blind spots)
And honestly, when a hits, even the smallest sound or faintest beam of light feels like an attack. Many people describe it as a storm inside the head—one that can last anywhere from a few hours to a couple of days.
Common Triggers (And Why They Matter)
You know what’s interesting? Migraines rarely happen “out of nowhere.” Most of the time, there’s a trigger hiding in the background.
1. Stress and Emotional Tension
Ever noticed how show up right after a long, exhausting week? That’s because stress causes chemical changes in the brain that can spark migraine episodes.
2. Sleep Disruptions
Too little sleep, too much sleep, or irregular patterns—your brain doesn’t love it.
3. Food Triggers
Certain foods can be sneaky culprits, such as:
-
Caffeine
-
Aged cheeses
-
Chocolate
-
Alcohol
-
Processed meats
Everyone’s different, so what triggers one person may not affect another at all.
4. Hormonal Changes
Many women notice migraines around their menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or menopause due to shifting hormone levels.
5. Environmental Factors
Bright lights, strong smells, loud noises, or even sudden weather changes can set things off.
Migraine vs. Headache: Why They’re Not the Same
A regular headache is usually just discomfort. A , though, feels more like a full-body event.
often include:
-
Throbbing pain, usually on one side
-
Sensory sensitivity
-
Nausea
-
Visual disturbances
Headaches typically:
-
Feel like pressure
-
Don’t usually limit daily activity
-
Respond quickly to simple pain relievers
So if your pain feels like it’s forcing you to lie down, close your eyes, or avoid noises—it’s probably leaning toward the migraine category.
Helpful Tips for Managing Migraines
Let’s be honest—there’s no miracle cure you can snap your fingers for. But there are practical ways to reduce the frequency and intensity.
1. Keep a Migraine Diary
Track what you ate, your stress level, sleep, and activities. Patterns often show up faster than you expect.
2. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration is a surprisingly common trigger.
3. Practice Relaxation
Try:
-
Deep breathing
-
Gentle stretching
-
Meditation
-
Light yoga
Your brain loves calm.
4. Create a Regular Sleep Routine
Consistency helps regulate your nervous system, which may reduce attacks.
5. Limit Screen Time When Migraine Feels “Close”
Blue light and long hours staring at screens can intensify symptoms.
6. Use Cold or Warm Compresses
Some people find relief with ice packs; others prefer warmth. Test both to see what your body responds to.
When Should You Seek Professional Help?
If start interfering with your daily life, come more frequently, or feel unusually intense, a healthcare professional can offer personalized guidance. You don’t have to struggle alone.
Conclusion
Migraine may feel overwhelming, but understanding them is the first step toward taking back control. The more you listen to your body—identifying triggers, practicing self-care, and building healthier routines—the easier it becomes to manage the storms before they even start.
So take it one step at a time. Your brain deserves patience, compassion, and care.
FAQs About Migraine
1. What causes migraines to start?
often begin due to triggers like stress, hormonal changes, certain foods, lack of sleep, or environmental factors.
2. How long does a typical migraine last?
A can last anywhere from 4 hours to 72 hours, depending on the person and the severity.
3. Can lifestyle changes help reduce migraines?
Yes—consistent sleep, hydration, stress management, and avoiding personal triggers can significantly reduce the frequency of attacks.
4. Are migraines hereditary?
They can be. Many people with have a family history of the condition.